Host Interface¶
All communications between the HSM and the Host Computer will
take place over UART at a baud rate of 115200. Said communications must
adhere to the protocol specified by the host tools and documented here. The
host_messaging library included in the example design provides an easy
interface to send messages to the host tools.
All communications between two HSMs will also take place over UART at a baud
rate of 115200, though the formatting of those messages can be adapted
according to the design.
The message structure is made of 4 components:
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
MAGIC |
1 byte |
Message start byte, ‘%’ |
OPCODE |
1 byte |
Indicates the type of message |
LENGTH |
2 bytes |
Length of the message body |
BODY |
Variable Length |
Actual message contents |
The length may be 0 in which case the message body will be empty. The first 3 components (MAGIC, OPCODE, and LENGTH) are considered the message header and are distinct from the rest of the message (BODY). All integer values (except in design-specific fields) are in little endian. The host tools accept nine types of messages:
Type |
Opcode |
Use |
|---|---|---|
List |
|
List files command/response |
Read |
|
Read file command/response |
Write |
|
Write file command/response |
Receive |
|
Receive file command/response |
Interrogate |
|
Interrogate files command/response |
Listen |
|
Listen command/response |
Ack |
|
Acknowledge the receipt of data |
Error |
|
Notify of an error/failure. Exits Host Tool |
Debug |
|
Provide debug information (ignored by testing framework) |
For example, a write command with a size of 0x20 bytes will have a header that looks like:
‘%W\x20\x00’.
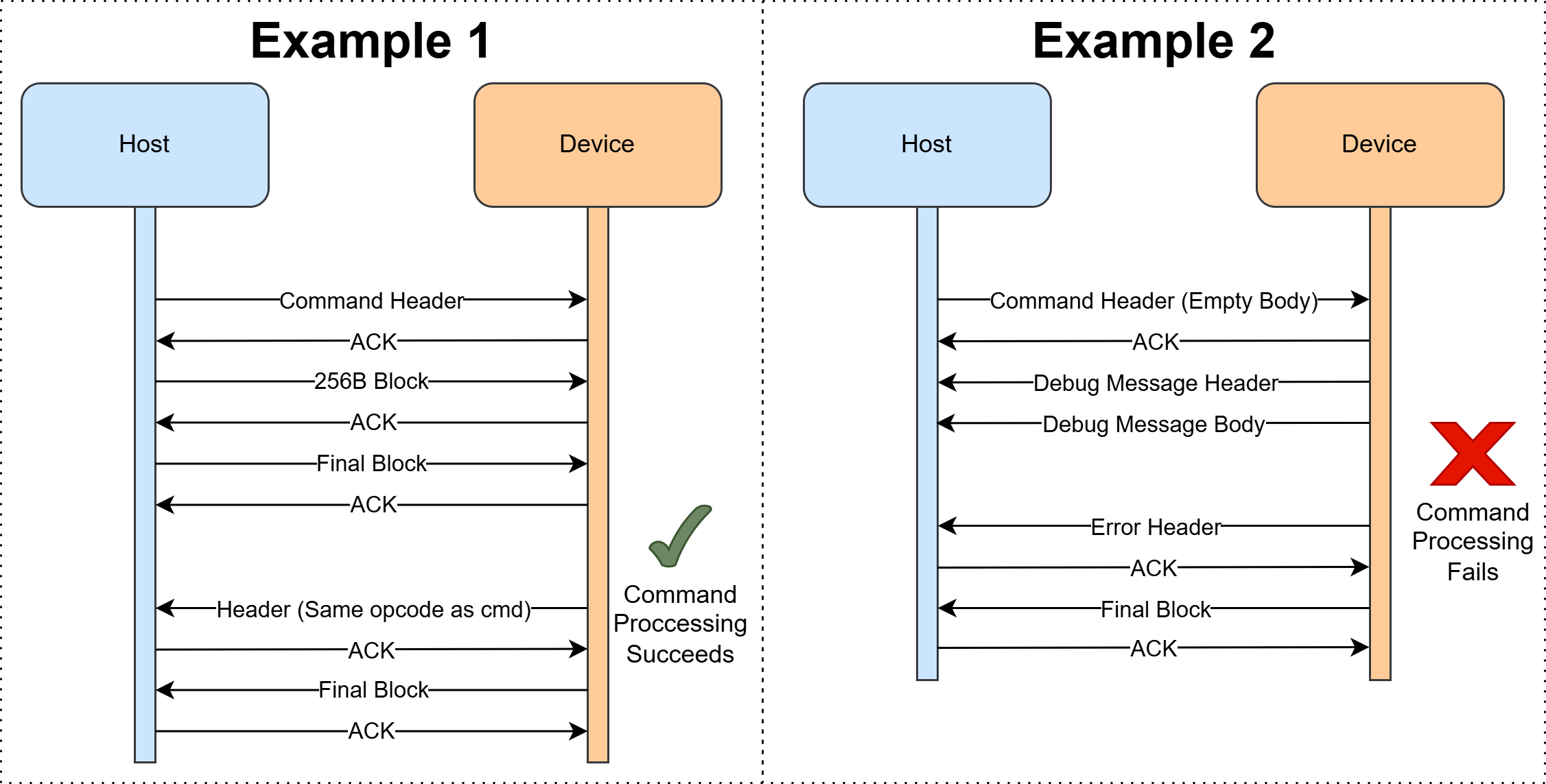
Except for debug messages, the Host Computer will initiate all communication with the HSM. An exchange of a message will start with the sender sending the 4 header bytes. The receiver will send an ACK indicating it is ready for more data. The sender will then send the content of the body 256 bytes at a time. After every 256 bytes, the receiver will send an ACK indicating it is ready for more data. The final chunk of data, regardless of whether it is 256 bytes long or less than that must also be ACKed.
The exception to this process is debug messages. When a HSM sends a debug message, the host will not ACK any portion of it.
When processing a command on the HSM fails, the HSM must respond with an error message type. The contents of the error do not matter. When processing a command on the HSM succeeds, the HSM must respond with a message type that is the same as the command (see below for contents).
List Files¶
This is a pin protected function. The list files functionality must return ALL files that the HSM contains. The body of the response will contain a list of files and their associated metadata.
Host Command¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Pin |
6 bytes |
The pin to authenticate the user |
HSM Response¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Num files |
32 bits |
Number of files on the device |
File Metadata |
Variable len |
An array of |
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Slot |
8 bits |
The slot in which the file is stored |
Group ID |
16 bits |
The group id of the file |
Name |
32 bytes |
The name of the file (null-terminated) |
Read File¶
This is a pin protected function. If the HSM has permissions to read the file, the HSM should return the file in the same format it was originally provided.
Host Command¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Pin |
6 bytes |
The pin to authenticate the user |
Slot |
8 bits |
The slot from which to read the file |
HSM Response¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
File Name |
32 bytes |
The name of the file (null-terminated) |
File Contents |
Variable len |
The contents of the file |
Write File¶
This is a pin protected function. If the HSM has permissions to write the group, the HSM should write the file to the device.
Host Command¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Pin |
6 bytes |
The pin to authenticate the user |
Slot |
8 bits |
The slot to write the file to |
Group ID |
16 bits |
The group id of the file |
Name |
32 bytes |
The name of the file (null-terminated) |
UUID |
16 bytes |
The UUID of the file |
Contents Length |
16 bits |
The length of the contents field |
File Contents |
Variable len |
The contents of the file (of the above length) |
HSM Response¶
The write response will have an empty body.
Listen¶
This is not a pin protected function. The HSM should prepare to receive an Interrogate or Receive message over UART1.
Host Command¶
The Listen command will have an empty body.
HSM Response¶
The Listen response will have an empty body.
Interrogate Files¶
This is a pin protected function. The HSM should reach out via UART1 to a neighbor HSM to receive a list of files on that device. The interrogate files functionality must return a list of all files that the neighbor HSM contains for which the local HSM has receive permissions. The body of the response will contain a list of files and their associated metadata. Communication between the two devices may be design-specific.
Host Command¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Pin |
6 bytes |
The pin to authenticate the user |
HSM Response¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Num files |
32 bits |
Number of files on the device |
File Metadata |
Variable len |
An array of |
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Slot |
8 bits |
The slot in which the file is stored |
Group ID |
16 bits |
The group id of the file |
Name |
32 bytes |
The name of the file (null terminated) |
Receive File¶
This is a pin protected function. The HSM should reach out via UART1 to a neighbor HSM to receive a file from that device. If the HSM has permissions to receive the group, the HSM should write the file to the device.
Host Command¶
Name |
Size |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Pin |
6 bytes |
The pin to authenticate the user |
Read Slot |
8 bits |
The slot on the neighbor HSM from which to read the file |
Write Slot |
8 bits |
The slot on the local HSM to which to write the file |
HSM Response¶
The Receive response will have an empty body.
Example¶
Suppose the host wants to issue the list command. It will first send the command header. Per the
spec, it will use an opcode of L and a size of 6. This makes the header ‘%L\x06\x00’.
After sending the header, the host will wait for an ACK (’%A\x00\x00’) from the HSM. The host
then sends a body containing the HSM PIN, say ‘123456’, and waits for the HSM to send another ACK
for receipt of the last (and only) chunk of the body. The host then waits for a response message
from the HSM.
Processing the list command succeeds on the HSM, so it will respond with the same message
type as the command. Let’s suppose the HSM has two files: File 1 in slot 3 with group 1234 and
File 2 in slot 5 with group 4321. Thus, the the total message size is 74 and the HSM will send
the header ‘%L\x4a\x00’. The host will respond with an ACK. Then the HSM will send the
command body:
char *msg = ""
"\x02\x00\x00\x00" // Number of files
"\x03" // Slot number of File 1
"\xd2\x04" // Group of File 1
"File 1\x00...\x00" // Name of File 1 (32 bytes long, ... expands to 24 null bytes)
"\x05" // Slot number of File 2
"\xe1\x10" // Group of File 2
"File 2\x00...\x00"; // Name of File 2 (32 bytes long, ... expands to 24 null bytes)
After sending the response contents, the HSM will wait for an ACK before attempting to receive the next command.